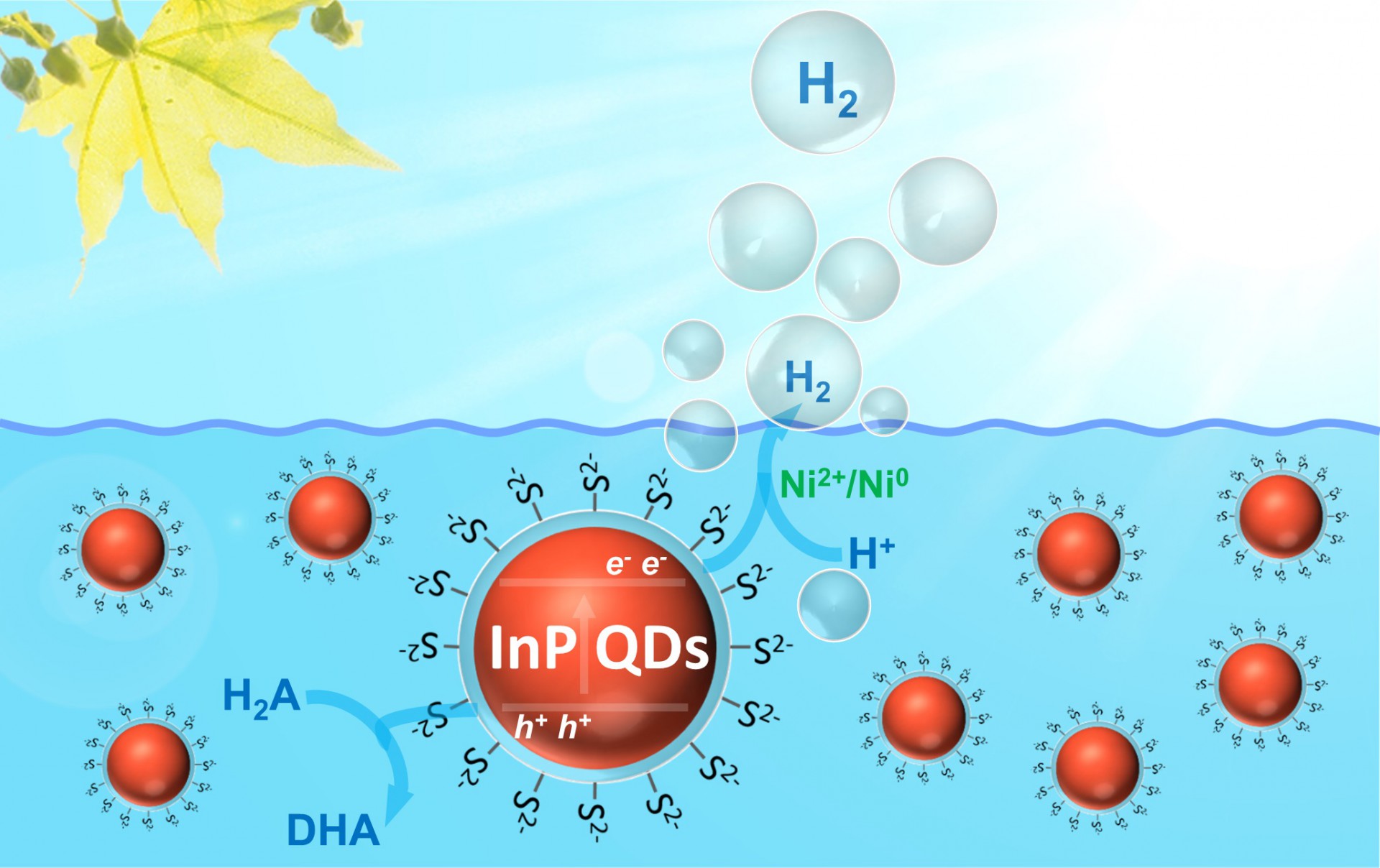
Recently, the latest achievement of ligand engineered all-inorganic InP and InP/ZnS colloidal quantum dots for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution was published on Nature Communications. In this work, the authors thus introduce InP QDs - a close competitor to CdSe QDs for display and bio-related applications - for effective photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Inspired by recent synthetic strategies towards InP QDs using aminophosphines as phosphorus source, the authors have successfully obtained a series of InP QDs with different excitonic absorption peaks. The authors demonstrated that all of them generated hydrogen under AM 1.5 illumination in a photocatalytic assay with ascorbic acid and nickel ions. Moreover, the authors have eliminated defects in the InP QDs through adding ZnS to their surface, which notably improved the efficiency of this hydrogen evolution system. According turnover numbers based on QDs were increased to 128,000, with a maximum internal quantum yield of 31 % (525 nm). These results identify InP QDs as competitive alternatives to CdSe QDs in artificial photosynthesis.
Full Article: Nature Communications 2018, 9, 4009.